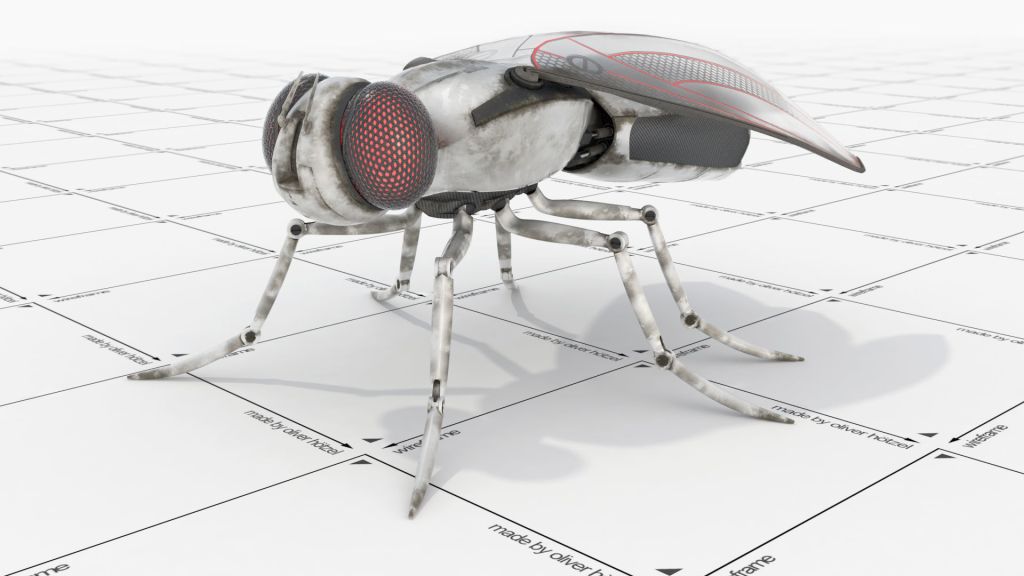
Nature’s Flight Secrets
The field of research surrounding robot flies has become a fascinating and rapidly advancing area of study, merging the disciplines of engineering, materials science, and robotics to create agile, autonomous flying robots that imitate the behaviors of real flies. Inspired by the flight capabilities of insects, particularly flies, scientists have embarked on a quest to unravel the mysteries of nature’s flight and apply them to various industries, leading to groundbreaking developments in the field of biomimetics.
Origins and Biomimetic Inspiration
The concept of robot flies originated from biomimetics, a field that aims to imitate and harness nature’s designs and processes to develop innovative technologies. Researchers were captivated by the agility, maneuverability, and adaptability of flies, which led to the idea of creating robotic counterparts capable of navigating complex environments. The project took flight in the early 2000s, driven by the desire to unlock the secrets of insect flight and utilize them for practical purposes.
The Multidisciplinary Approach
Developing a robot fly requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise in engineering, materials science, and robotics. The primary focus is on designing wings that can flap and generate lift, closely mimicking the flight of real flies. To achieve this, lightweight materials such as carbon fiber or thin polymer films are used to construct the wings, ensuring durability and the ability to produce the necessary thrust. Small motors or actuators drive the wing movements, replicating the intricate motions of fly wings with remarkable precision.
Navigation and Sensing
Robot flies are equipped with a range of sensors and instruments to navigate and perform tasks. These include cameras for visual perception, infrared sensors for obstacle detection, and gyroscopes and accelerometers for stability and orientation control. Some advanced robot flies even incorporate artificial intelligence algorithms, enabling them to make autonomous decisions and adapt to changing conditions in real-time.
Versatile Applications
While surveillance and reconnaissance have been the primary applications of robot flies, their potential uses extend far beyond these domains. For example, they can be employed to monitor air quality, collecting data on pollution levels and aiding in environmental research. Robot flies can also study insect behavior in their natural habitats, providing valuable insights into ecological systems. By observing and analyzing the flight patterns and behaviors of real flies, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of their role in pollination, ecosystem dynamics, and even disease transmission.
Revolutionizing Agriculture
In the agricultural sector, robot flies can assist in crop monitoring, pollination, and pest control. By mimicking the behavior of pollinators like bees and flies, they can help ensure optimal pollination rates, leading to increased crop yields. Additionally, robot flies equipped with sensors can detect and identify pests or diseases in crops, allowing for targeted interventions and reducing the need for harmful pesticides.
Infrastructure Inspection
In disaster-stricken areas or hazardous environments, robot flies can play a crucial role in search and rescue operations. They can navigate through debris, search for survivors, assess damage, and provide real-time information to aid in rescue efforts. Their small size and agility allow them to access areas that may be inaccessible to larger drones or human rescuers. Furthermore, robot flies can be equipped with specialized sensors to detect hazardous substances or monitor environmental conditions, providing valuable data for emergency response teams.
Additionally, robot flies can inspect critical infrastructure such as bridges, towers, and pipelines, navigating complex structures and capturing high-resolution images or videos for maintenance and safety purposes. By autonomously inspecting these structures, they can identify potential issues or weaknesses before they become major problems, ensuring the safety and longevity of infrastructure assets.
Ethical Considerations
Despite significant advancements, there are still challenges in the development of robot flies. Power supply and energy efficiency are critical concerns due to the limited onboard power capacity of small robots. Researchers are actively exploring innovative solutions, such as energy harvesting from the environment or improved battery technologies, to address these challenges. Additionally, controlling the flight dynamics and stability of such small robots requires sophisticated control algorithms and sensor integration, which continue to be areas of active research and development.
Ethical considerations also surround the use of robot flies, particularly in terms of privacy and surveillance. Striking a balance between the potential benefits and the invasion of privacy is a crucial aspect that needs to be addressed as these technologies continue to advance. Regulations and guidelines must be established to ensure responsible and ethical use of robot flies in various applications.
Unlocking the Future Potential
In conclusion, the field of robot flies has emerged as a captivating and rapidly evolving area of study, drawing inspiration from the flight capabilities of insects. Through a multidisciplinary approach, researchers have made significant progress in developing agile and autonomous flying robots that mimic the behaviors of real flies. While surveillance and reconnaissance have been the primary applications, the potential uses of robot flies extend to various industries, including environmental monitoring, agriculture, disaster response, and infrastructure inspection. However, challenges such as power supply and flight control still need to be overcome. As technology continues to advance, the future of robot flies holds great promise in revolutionizing industries, solving complex problems, and contributing to a more sustainable and efficient world.